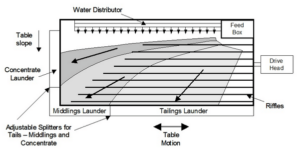
When it comes to separating gold from ore, beneficiation processes are key. Start with crushing and grinding to break down the ore into fine particles. From there, gravity separation methods—like using a shaker table or sluice box—help extract denser gold particles .
For finer gold, techniques like flotation or cyanidation are employed. Flotation uses chemicals to attach gold to air bubbles, while cyanidation dissolves gold for extraction .
These processes make gold recovery more efficient, turning even low-grade ores into valuable resources. Ready to start your gold journey? Beneficiation is where success begins!”
This short covers essential gold beneficiation processes, emphasizing efficient gold recovery.
Visit aurummeum.com for all the gold news and reports you could hope for. Contact us at operations@aurummeum.com to get connected to your personal Gold Advisor who will walk you through the process of owning gold the way YOU want.
Beneficiation is a critical step in the mining and mineral processing industry, involving the extraction and enhancement of valuable minerals from ores. The goal is to improve the quality and concentration of the valuable material by removing impurities or gangue, thus making the mineral economically viable for further processing or direct use in various applications. The process can involve several stages, including crushing, grinding, separation, and sometimes chemical treatments, depending on the type of mineral being extracted.
1. Types of Beneficiation Techniques:
• Physical Beneficiation: This method involves mechanical processes like crushing and grinding to break down the ore into smaller particles. Once the ore is ground, methods such as gravity separation, magnetic separation, and froth flotation are used to concentrate the valuable minerals. Gravity separation, for example, exploits the difference in the density between the valuable minerals and the gangue, while magnetic separation uses the magnetic properties of the ore.
• Chemical Beneficiation: In this method, chemical agents like acids or reagents are used to dissolve and separate valuable minerals from waste materials. An example is leaching, commonly used in gold beneficiation. During cyanide leaching, for example, gold is dissolved in a cyanide solution and then precipitated out.
• Hydrometallurgy and pyrometallurgy are also employed in chemical beneficiation, depending on the mineral being processed.
2. Stages of Beneficiation:Beneficiation can be broken down into a few main stages:
• Comminution: This involves the physical reduction of large rocks into smaller particles via crushing and grinding, making the ore easier to handle and process.
• Concentration: Various separation techniques are used here, such as froth flotation, where the ore is mixed with water and chemicals to form frothy bubbles that carry the valuable minerals to the surface.
• Dewatering: After concentration, the material often needs to be dried or dewatered. This stage is vital to remove excess moisture before further processing or transportation.
3. Importance and Environmental Considerations:
Beneficiation not only increases the efficiency of mining operations by concentrating valuable minerals but also reduces waste and transportation costs. Additionally, it can help reduce the environmental impact by minimizing the volume of material that must be handled and processed. However, if not managed properly, beneficiation can have significant environmental consequences. For example, the chemicals used in the process, such as cyanide in gold extraction or acids in other forms of leaching, can lead to toxic waste and contamination of local ecosystems if not contained and treated responsibly. Tailings—waste materials left after extraction—can also pose a risk if not stored correctly, as they may contain harmful substances or heavy metals.
In conclusion, beneficiation is essential in making mining economically viable and more sustainable by reducing the quantity of material needing to be processed. However, careful environmental management is required to minimize its potential negative impacts on surrounding ecosystems and communities.